Everything you need to know about docker volumes - Docker tips and tricks
Everything you need to know about docker volumes - Docker tips and tricks
Consider a scenario where you develop a Nodejs Application with MongoDB as a database. your application stores the data in MongoDB and everything goes well.
After some point of time, you want to automate the process of deployment. so, everytime Pull request is merged into master branch. you want to create a new docker container to serve your application.
One of the main challenges that you face here is, everytime you delete an existing container. your mongodb data will also be deleted. it will be a problem while using a docker.
To overcome this problem, we need to use Docker Volumes. Let’s learn everything about docker volumes in this guide.
What is Docker volume
Docker volume is a persistent data storage mechanism to store the data in docker. before volumes, docker uses bind mounts to store data in the container. bind mounts are dependent on the directory structure of host machine.
Let’s look at this in detail to understand it further. As you know, docker runs a isolated containers with separate process that shares the file system and hardware from the host machine . Whenever you create a container, it mounts a directory with the container to run our application.
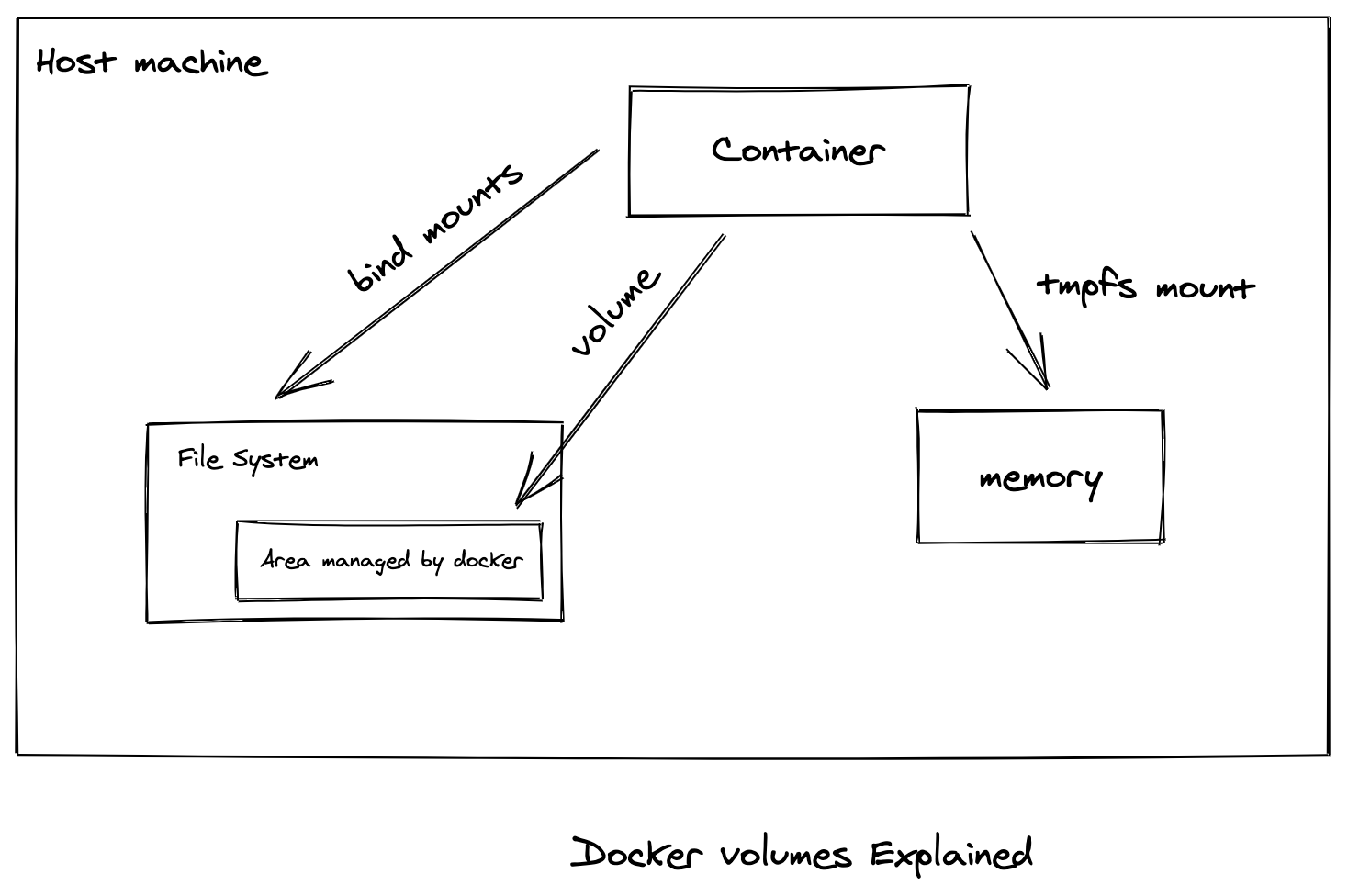
File system managed by container can not be shared with other containers. To create a directory managed by container. we use bind mounts.
problem with bind mounts is, it is not persistent. once we remove the container, docker deleted the respective file directory of the respective container.
To solve this, we use docker volumes, one of the main differences are docker manages volume directly. In that way, even if you delete the container. data will be persistent.
Getting started with docker volume
Create a Volume
To create a volume in docker, use the command,
docker volume create <VOLUME NAME>
Note: warning will not occur for your docker configuration.
List Volume
Once you create a volume, you can list all the docker volume using the command,
docker volume lsRemove a volume
To remove a volume from docker, you can use the follow command,
docker volume rmRemove all unused volume
you can also remove all unused volume from docker using the command,
docker volume prunedocker volume - example
Let’s take an example to learn about docker volumes. here, we will take a two nodejs application which shares a same docker volume. both will contains API to write and read a file. let’s see if docker volume can be shared between two container.
At the end of this guide, i have a real world example as an exercise for you. so, stay tuned
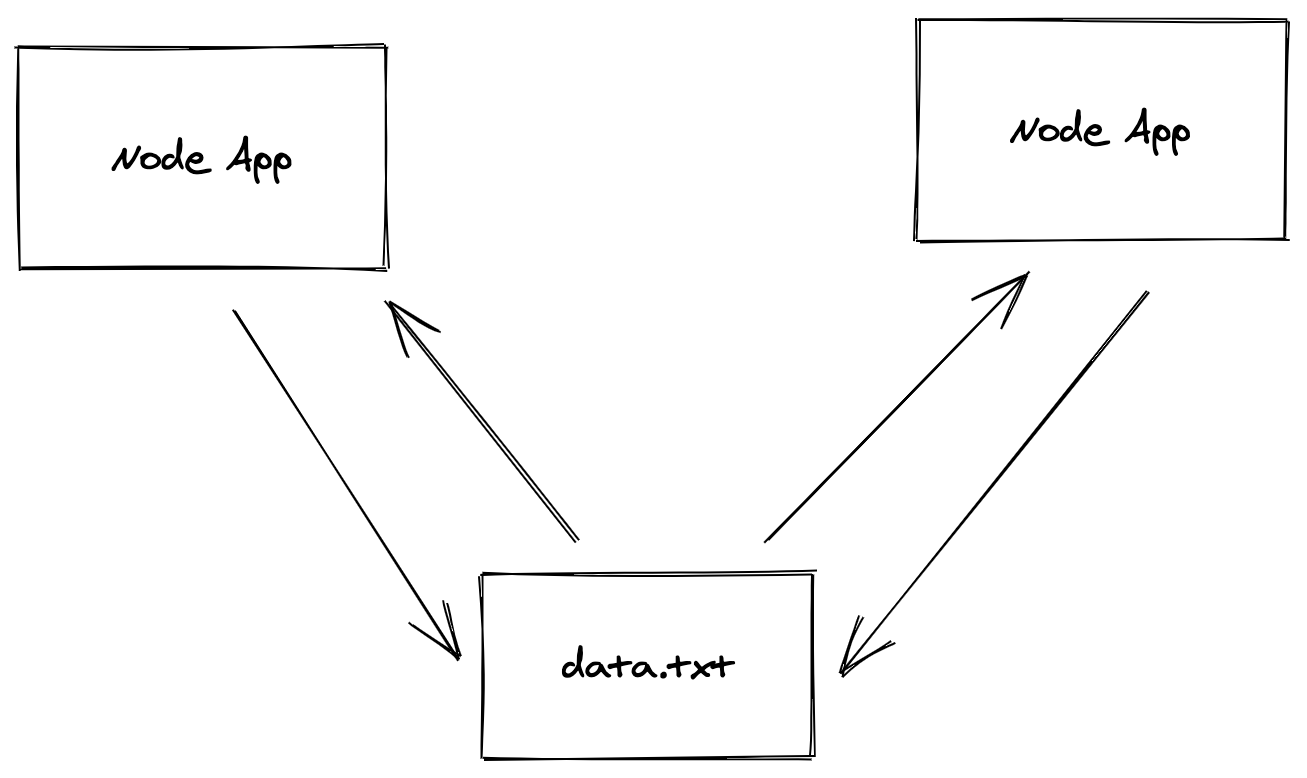
let’s build this application and use docker volume to store the data. create a application with npm init and add app.js
const express = require("express");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const path = require("path");
const fs = require("fs");
const app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
const dataPath = path.join(process.env.DATA_PATH || "./data.txt");
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Welcome To docker volume");
});
app.get("/data", (req, res) => {
let data = fs.readFileSync(dataPath);
data = data.toString();
res.status(200).send(data);
});
app.post("/add", (req, res) => {
const data = req.body.text;
fs.writeFileSync(dataPath, data);
res.status(201).send({ success: true });
});
async function start() {
app.listen(3001, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on PORT ${3001}`);
});
}
start();Here, we add two API’s add and data where add writes the request data to file. and data GET API returns the data.
let’s create a Dockerfile for our application.
FROM node:alpine
WORKDIR /src
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm install
COPY . .
CMD ["node","app.js"]If you’re beginner to docker world, i recommend you to checkout this article
After that, you need to build docker image for our application to run it in container.
docker build -t <TAG NAME> .once you build docker image for our app. you need to run it in the container. here’s where you need to mount docket volume for your application container.
Mounting a docker volume
To mount a docker volume with container, you need to add the --mount flag in docker run command.
docker run --mount source=[volume_name],destination=[path_in_container] [docker_image]source specifies the name of the volume and destination specifies the path in container.
For the above application, you need to specified it as,
docker run -d --env DATA_PATH=/data/data.txt --mount type=volume,src=file-st,target=/data -p 3001:3001 <IMAGE TAG>it will mount the volume with specified container path. now, anything you write and read will be from the docker volume.
Let’s create an another application which shares the same docker volume to check whether it is working. you can use the same setup by changing the port in the application and docker container.
app.listen(3002, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on PORT ${3002}`);
});docker run command will be
docker run -d --env DATA_PATH=/data/data.txt --mount type=volume,src=file-st,target=/data -p 3002:3002 ganeshmani009/volume-app-two:latestNow, that we have a two application running with shared docker volume. let’s try to write a file and see if it gets reflected in the another application.
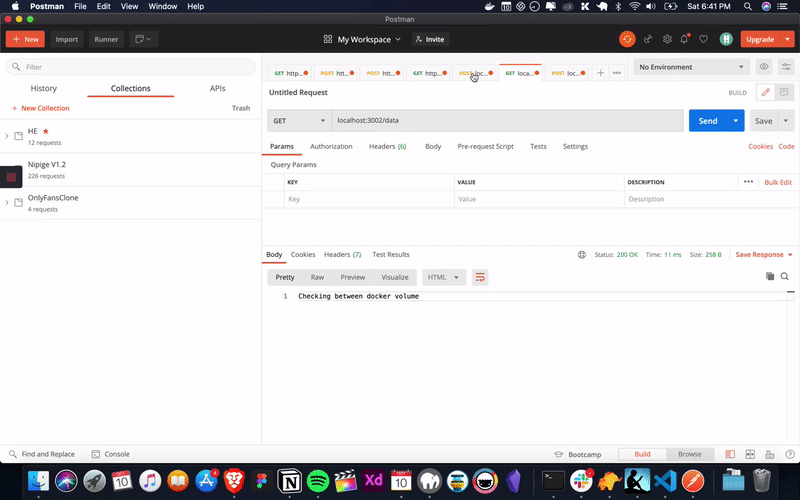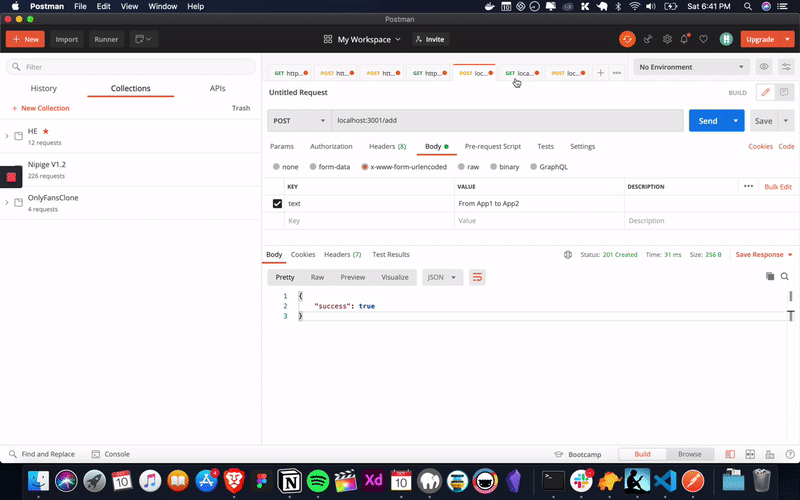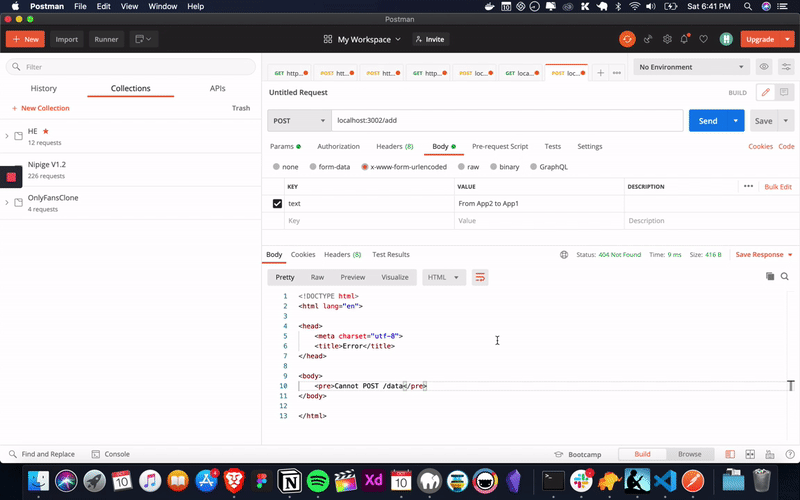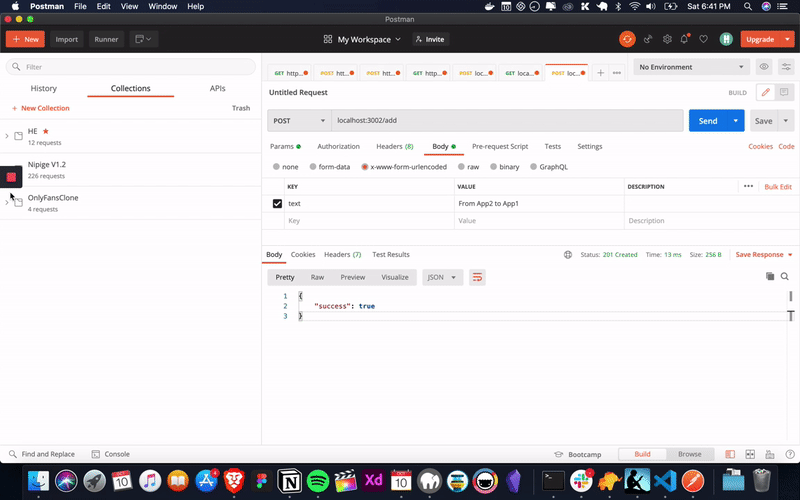
Alright. our applications works the way we expected. now, it’s time to do our exercise with a real world example.
Real world Example
Here’s the task that you need to do,
- Create a Simple Todo Nodejs Application with MongoDB connection to store the data.
- Pesist the Mongodb Data with Docker volume.
- Create an another Nodejs Application to read the Todo from MongoDB and show it as logs.
Conclusion
i recommend you to try this real world scenario to get hands-on experience on the docker volumes. having a knowledge on docker as a web developer become vital in the current software development world. Happy coding :-)